SIDD Simulator of Individual Dynamic Decisions

Downloads.

Model variants.
All versions of SIDD can be downloaded from this page; click on a model version to start. Each download delivers a single installer file; details concerning model installation can be found here. Please note that the model downloads accessible from this page include limited access to the underlying source code. Enjoy! NOTE: Versions of the model prior to 3.21 (03 Mar 2018) are parameterised for the UK to data reported by a withdrawn public access file of the Wealth and Assets Survey.

Code snippets.
Selected components of the model code, organised by subheading, can be downloaded here (by clicking on the blue down arrow down-load icons). The code snippets provided here are not subject to licensing, and can be used in any way (including porting into third-party applications). This code is made available without warranty, and subject to the usual disclaimer indemnifying the developers from any and all associated damages incurred.Optimisation
Search for a local minimum in a single dimension
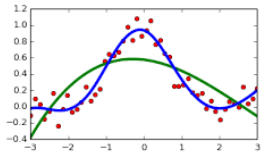
Uses Brent’s method for finding a (local) minimum in a single dimension.Search for a local minimum in n dimensions
Uses Powell’s method to finding a (local) minimum in multiple dimensions, via calls to Brent’s method (see above).Linear evaluation of a zero using only function calls
Uses the Bus-Dekker algorithm to search for a zero to a function along a single dimensionMiscellaneous
Gauss Hermite Quadrature
Given the order of the Hermite polynomial, this subroutine returns vectors for abscissae and weights implied by the Gauss Hermite Quadrature.Function to calculate the cumulative Normal density
Given an observation X, and the mean and standard deviation, the function evaluates the probability associated with a value less than or equal to X.Function to calculate the inverse of the cumulative Normal
The function returns the value X, under which a normal Given a probability P, and the mean and standard deviation, the function evaluates the value X associated with a value less than or equal to X.FORTRAN communications with Excel
Code managing read and write routines between FORTRAN and Excel. FORTRAN communication is undertaken by C# routines accessed via C++ native and a C/CLI wrapper. While an Intel Fortran module wizard exists to facilitate direct communication with Excel via COM (the Autodice example), we have found the routines generated by the wizard to be unreliable, which motivated development of the code provided here. C# was selected for Excel communication because it is a low-level Microsoft language, which we hope will provide reliable communications with Excel into the future. The C/CLI wrapper provides a useful bridge between managed (C#) and unmanaged (C++) code, and communication between C/C++ and FORTRAN is straight-forward. The code that is provided here could be easily adapted to omit the FORTRAN extension. A full walk-through of the Visual Studio 2015 Solution set-up is also provided to clarify compiler settings, along with the associated VS2015 source code.Interpolation
Linear spline interpolation.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in a single dimension.Cubic spline interpolation.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in multiple dimensions - uses calls to Brent’s method (see above).




















Latest version:
Older versions:


Model description:














User manual:
SIDD Simulator of Individual Dynamic Decisions

Downloads.

Model variants.
All versions of SIDD can be downloaded from this page; click on a model version to start. Each download delivers a single installer file; details concerning model installation can be found here. Please note that the model downloads accessible from this page include limited access to the underlying source code. Individuals who would like access to the full source code should submit a request via the form found here. Enjoy! NOTE: Versions of the model prior to 3.21 (03 Mar 2018) are parameterised for the UK to data reported by a withdrawn public access file of the Wealth and Assets Survey.



Code snippets.
Selected components of the model code, organised by subheading, can be downloaded here (by clicking on the blue down arrow down-load icons). The code snippets provided here are not subject to licensing, and can be used in any way (including porting into third-party applications). This code is made available without warranty, and subject to the usual disclaimer indemnifying the developers from any and all associated damages incurred.

Optimisation
Brent’s method.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in a single dimension.Powell’s method.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in multiple dimensions - uses calls to Brent’s method (see above).Linear evaluation of a zero using only
function calls
Uses the Bus-Dekker algorithm to search for a zero to a function along a single dimension
Interpolation
Linear spline interpolation.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in a single dimension.Cubic spline interpolation.
A method for finding a (local) minimum in multiple dimensions - uses calls to Brent’s method (see above).
Miscellaneous
Gauss Hermite Quadrature
Given the order of the Hermite polynomial, this subroutine returns vectors for abscissae and weights implied by the Gauss Hermite Quadrature.Function to calculate the cumulative
Normal density
Given an observation X, and the mean and standard deviation, the function evaluates the probability associated with a value less than or equal to X.Function to calculate the inverse of the
cumulative Normal
The function returns the value X, under which a normal Given a probability P, and the mean and standard deviation, the function evaluates the value X associated with a value less than or equal to X.FORTRAN communications with Excel
Code managing read and write routines between FORTRAN and Excel. FORTRAN communication is undertaken by C# routines accessed via C++ native and a C/CLI wrapper. While an Intel Fortran module wizard exists to facilitate direct communication with Excel via COM (the Autodice example), we have found the routines generated by the wizard to be unreliable, which motivated development of the code provided here. C# was selected for Excel communication because it is a low-level Microsoft language, which we hope will provide reliable communications with Excel into the future. The C/CLI wrapper provides a useful bridge between managed (C#) and unmanaged (C++) code, and communication between C/C++ and FORTRAN is straight-forward. The code that is provided here could be easily adapted to omit the FORTRAN extension. A full walk-through of the Visual Studio 2015 Solution set-up is also provided to clarify compiler settings, along with the associated VS2015 source code.
Downloads can only be accessed via the desktop variant of this website.